News
Launched in 1999 and updated regularly, Statewatch News includes our own reporting and writing as well as articles, announcements, documents and analyses from elsewhere on civil liberties, EU policies and state practices. You can receive updates in your inbox by signing up to our mailing list, or use our RSS feed to get instant alerts.

Algeria: Migrants face raids, mass expulsions, and hate speech
In recent years, there has been an alarming rise in hate speech and persistent incitement against migrants from sub-Saharan Africa in Algeria. Racist rhetoric is widely circulated in some media outlets and on social media, underpinning a general climate of marginalisation and discrimination. A joint letter signed by 20 organisations from Europe and Africa calls on the Algerian authorities to halt arbitrary mass expulsions of migrants, and to end policies that criminalise civil society organisations standing in solidarity with them.

"Deep concern" over EU's plan "to weaken or circumvent encryption"
The European Commission should reinforce and support that enable private communication, says a joint letter signed by almost 90 organisations, companies and technical experts. The Commission's recent Internal Security Strategy says there is a need to "enable law enforcement authorities to access encrypted data in a lawful manner," alongside a host of other proposals on policing and security. Statewatch is a signatory of the letter.

Turkey: Political prisoners must be freed as part of drive to end prison overcrowding
A statement signed by 12 organisations, including Statewatch, calls on the Turkish government to release political prisoners as part of a push to stop prison overcrowding. Political prisoners are currently exempt from the scheme due to anti-terrorism laws passed in 2020 and 2023. Those affected include lawyers, journalists, politicians, artists, judges and prosecutors, and human rights defenders.

EU: Business deregulation plans will undermine data protection rights
More than 120 organisations, including Statewatch, are calling on the EU to keep the General Data Protection Regulation in place, as the European Commission announces plans to remove certain provisions of the law in the name of removing 'red tape' for businesses. The signatories express concern that the proposed changes "could instead roll back key accountability safeguards and with them, the accountability principle itself."

Deportation camps: EU member states want to “prevent judicial scrutiny”
Agreements between the EU and non-EU states on so-called “return hubs” should be “framed in flexible way” to “prevent judicial scrutiny.” This is according to a document produced by the Polish Presidency of the Council in February, obtained and published by Statewatch.
France: Flaws and injustices of 'predictive policing' laid bare in new report
As part of a European initiative coordinated by Statewatch, La Quadrature du Net has published an English translation of its report on the state of predictive policing in France. In light of the information gathered, and given the dangers these systems carry when they incorporate socio-demographic data as a basis for their recommendations, La Quadrature calls for a ban.
EU’s secretive “security AI” plans need critical, democratic scrutiny, says new report
The EU is secretively paving the way for police, border and criminal justice agencies to develop and use experimental “artificial intelligence” (AI) technologies, posing risks for human rights, civil liberties, transparency and accountability, says a report published today by Statewatch.

Belgium: New report calls for a ban on 'predictive' policing technologies
Following an investigation carried out over the past two years, Statewatch, the Ligue des droits humains and the Liga voor mensenrechten, jointly publish a report on the development of ‘predictive’ policing in Belgium. There are inherent risks in these systems, particularly when they rely on biased databases or sociodemographic statistics. The report calls for a ban on ‘predictive’ systems in law enforcement.

UK: Over 1,300 people profiled daily by Ministry of Justice AI system to ‘predict’ re-offending risk
Over 20 years ago, a system to assess prisoners’ risk of reoffending was rolled out in the criminal legal system across England and Wales. It now uses artificial intelligence techniques to profile thousands of offenders and alleged offenders every week. Despite serious concerns over racism and data inaccuracies, the system continues to influence decision-making on imprisonment and parole – and a new system is in the works.
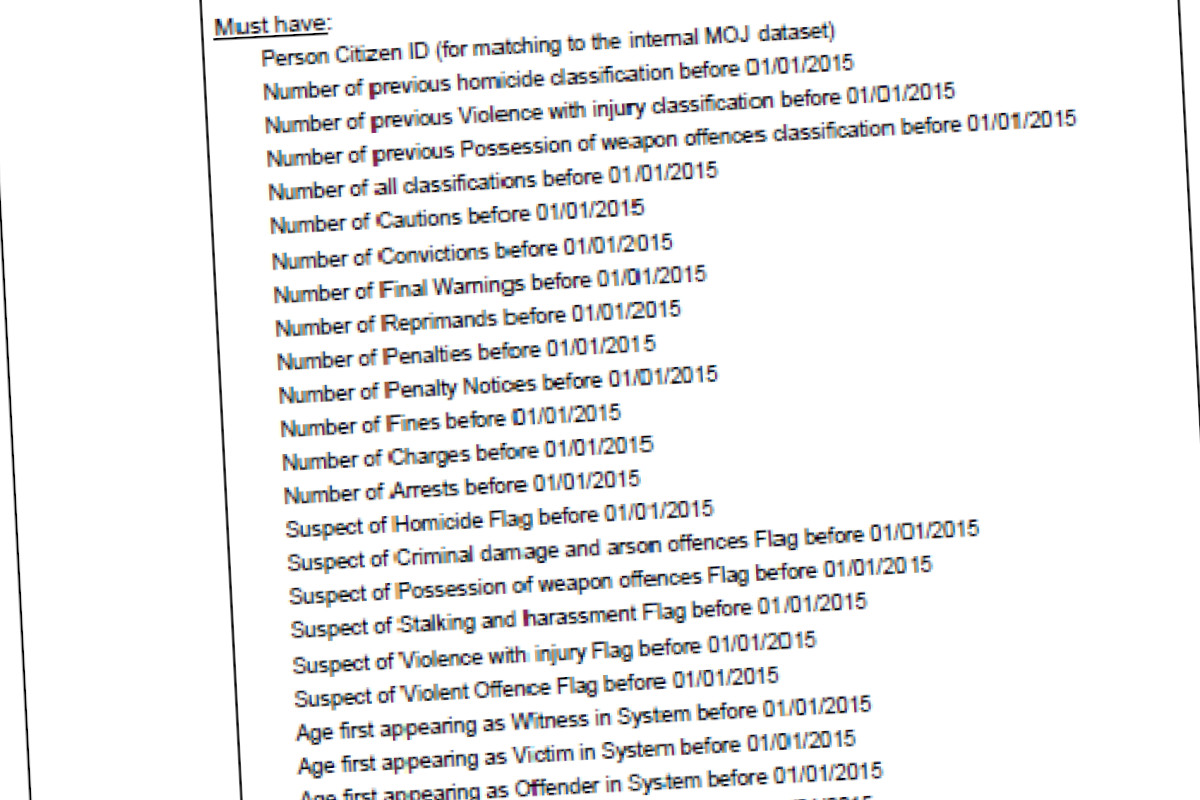
UK: Ministry of Justice secretly developing ‘murder prediction’ system
The Ministry of Justice is developing a system that aims to ‘predict’ who will commit murder, as part of a “data science” project using sensitive personal data on hundreds of thousands of people.

UK government wants to legalise automated police decision-making
A proposed law in the UK would allow police decisions to be made solely by computers, with no human input. The Data Use and Access Bill would remove a safeguard in data protection law that prohibits solely automated decision-making by law enforcement agencies. Over 30 civil liberties, human rights, and racial justice organisations and experts, including Statewatch, have written to the government to demand changes.

Swedish parliament urged to reject law that would "greatly undermine security and privacy"
The Swedish parliament is benig urged to reject a law that would "force companies to store and provide law enforcement with access to their users’ communications, including those that are end-to-end encrypted." The law, designed to strengthen police powers, would "create vulnerabilities that criminals and other malicious actors could readily exploit," says the letter. More 230 organisations and individuals from more than 50 countries have signed the letter, including Statewatch.

Serbia: Mass protests continue despite government repression
Almost 140 organisations from across Europe and beyond have expressed their solidarity with people in Serbia protesting against the government. An open letter condemns the Serbian government’s “effort to silence critical voices and suppress fundamental freedoms,” in response to nationwide protests sparked by the collapse of a train station. Statewatch has signed the letter.

EU officials discuss banning anonymous use of mobile phones
The Polish government has suggested new EU rules to ban the anonymous purchase of prepaid SIM cards for mobile phones.“The main threat associated with prepaid SIM cards is anonymity,” says a document obtained by Statewatch. Extensive research has found no evidence that bans on anonymous purchases of SIM cards contribute to reducing crime.

Call to reject new EU laws that "criminalise migrants and human rights defenders"
An open letter to the EU demands action to end the criminalisation of migrants and those who stand in solidarity with them. More than 100 signatories, including Statewatch, condemn proposed reforms to EU laws on migrant smuggling and call for an urgent change of approach.

Northern Ireland: How a 1980s state killing cover-up is still relevant today
A review of ‘Decades of Deceit: The Stalker Affair and its Legacy’ by Paddy Hillyard (Beyond the Pale Books, 2024).

From Malpensa to Tel Aviv: Italian police use Israeli software to spy on anti-deportation activsts
In March last year, four people were arrested after stopping a deportation flight to Morocco leaving Milan's Malpensa airport. When they got their phones back from the police, they found a strange file – one connected with spying products designed by the Israeli firm Cellebrite.

Italian police are “misleading” people about Schengen entry bans, says internal EU report
The Italian police are providing “misleading” information to people who ask whether there is a Schengen entry ban against them, says an internal EU report obtained by Statewatch. The document also says the country’s data protection authority cannot properly supervise the use of two huge EU databases.

EU: Digital and migrant rights groups call for "full rejection" of new anti-smuggling powers
Two new laws against migrant smuggling should be rejected by EU legislators, says a position paper published today. The paper, by the #ProtectNotSurveil coalition, analyses two proposals: an update of a 20-year old law on criminal penalties for migrant smuggling; and new rules to give police agency Europol more powers. The approach adopted by the EU "will not provide the care and protection people need, but only aggravate the criminalisation and dehumanisation of people on the move," argues the paper. Statewatch is a member of #ProtectNotSurveil and supported the drafting of the paper.
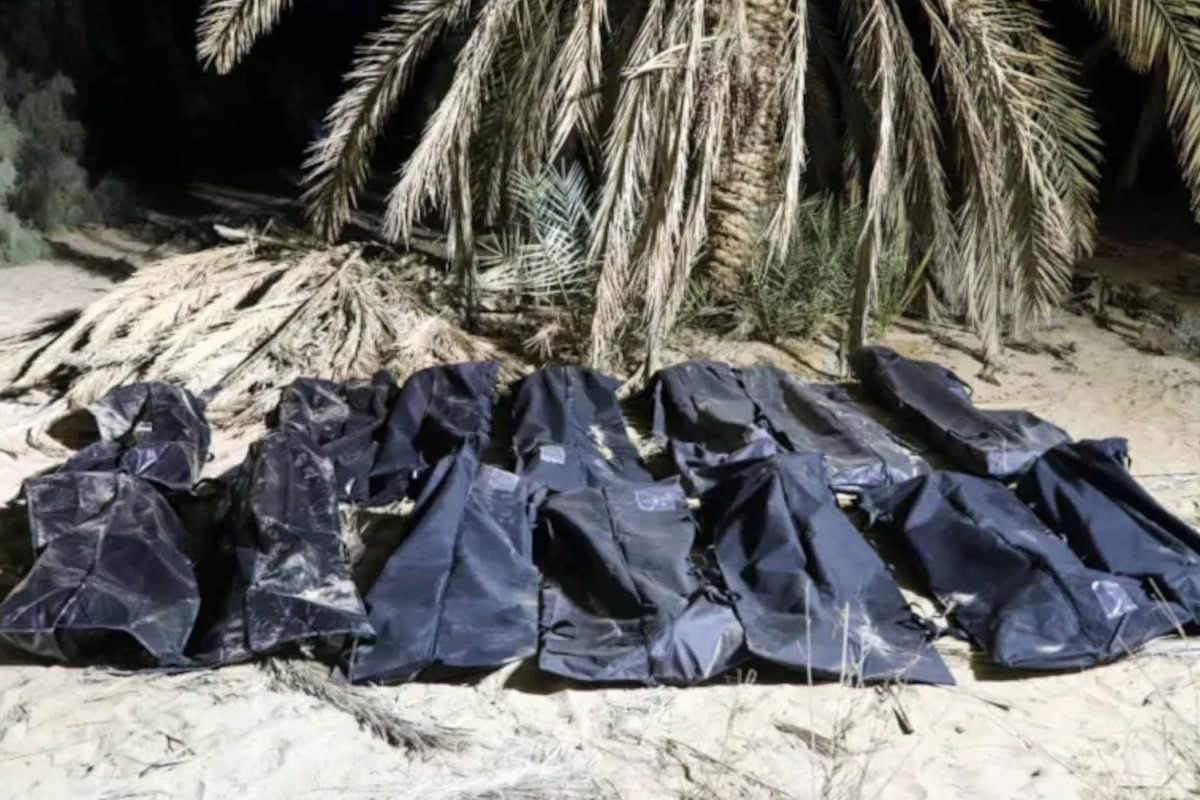

Libya: After discovery of mass graves, EU funding should "save lives and open up safe routes"
More than 30 organisations, including Statewatch, have called on the European Commission to use its funding for immigration control in Libya "to save lives and to provide alternatives to dangerous journeys." The call comes after the discovery of two mass graves in Libya, containing the bodies of almost 50 people believed to have been migrants and refugees.
Spotted an error? If you've spotted a problem with this page, just click once to let us know.